One of the key areas of focus in osteopathy is the diaphragm, a muscle often associated with breathing but with far-reaching implications for overall health and well-being.
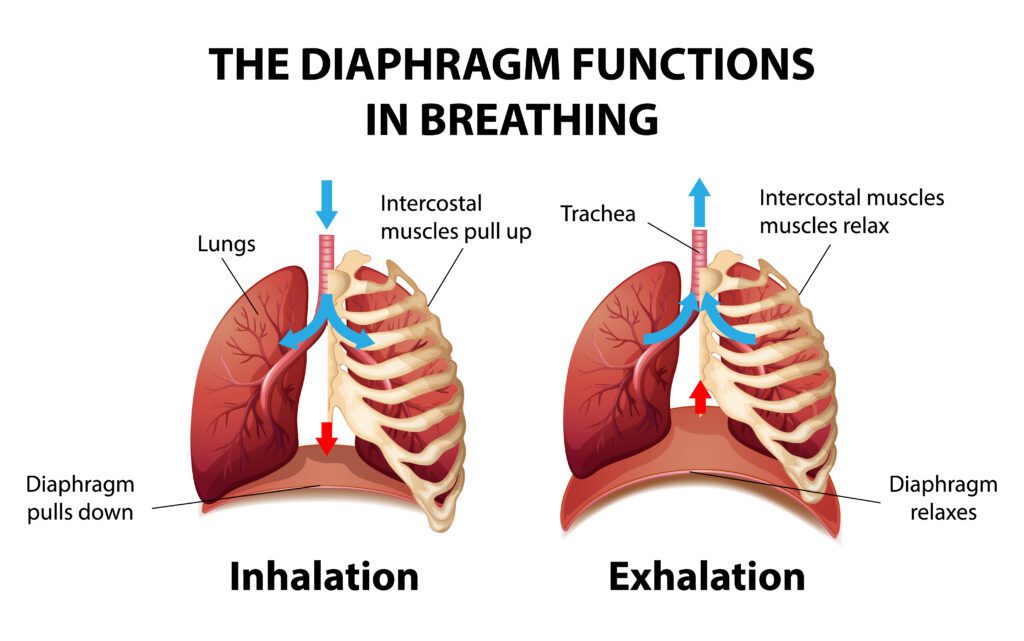
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the ribcage, separating the chest from the abdominal cavity. Its primary function is in the process of breathing. When we inhale, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, creating more space in the chest cavity and allowing the lungs to fill with air. Exhalation causes the diaphragm to relax and return to its dome shape, pushing air out of the lungs.
Inefficient or restricted diaphragm movement can lead to respiratory problems, such as shallow breathing, reduced lung capacity, and increased stress on secondary respiratory muscles. However, the diaphragm is more than just a breathing muscle; it is a dynamic structure with connections to various parts of the body, including the spine, ribs, and organs. This is where you and the practitioners at Blackburn Allied Health Group come into play.
If my diaphragm isn’t functioning properly, how will this affect me?
- Respiration and Circulation: Shallow breathing, reduced oxygen intake, and altered circulation can have a cascading effect on various systems, potentially contributing to fatigue, tension, and other health issues.
- Musculoskeletal Health: The diaphragm is connected to the spine and ribcage. This can create tension and misalignment in the spine, ribs, and surrounding tissues leading to pain and discomfort.
- Visceral Health: The diaphragm attaches to various organs, including the liver, stomach, and heart. This can affect the mobility and function of these organs, potentially contributing to digestive issues, heartburn, and other visceral problems.
- Emotional Well-being: The diaphragm’s role in breathing extends to our emotional well-being as well. Shallow breathing patterns, often associated with diaphragmatic dysfunction, can contribute to stress, anxiety, and tension.
What can you do about it?
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Practicing to strengthen and improve the flexibility of your diaphragm. This technique involves deep, slow breaths that engage the diaphragm fully. It’s an effective way to reduce stress, improve oxygen exchange, and enhance lung function.
- Maintain Good Posture: Slouching or poor posture can compress the diaphragm, making it harder for it to contract and expand properly.
- Physical Activity: Cardiovascular activities, such as jogging, swimming, or cycling, can help increase the capacity of your lungs and make your diaphragm stronger.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking damages the respiratory system and can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other respiratory issues.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to shallow breathing patterns that do not fully engage the diaphragm. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can promote healthier breathing.
- COME SEE THE OSTEO!!! Treatment for the diaphragm involves hands-on techniques aimed at assessing and addressing any restrictions or dysfunctions. This is to help release tension and improve muscle and organ function and mobility.
The diaphragm plays a central role in promoting overall health and well-being. By addressing diaphragmatic dysfunction, we can help individuals achieve better breathing, improved musculoskeletal health, and enhanced emotional well-being.
If you’re experiencing issues related to breathing, musculoskeletal discomfort, or visceral problems, come see us at Blackburn Allied Health Group to evaluate the role of your diaphragm in your overall health and provide tailored treatment to address any concerns.



